Introduction
When dealing with situations such as ffmpeg audio modulation or pause/resume actions, an ffmpeg-like backend might not handle it effectively due to the lack of breakpoint timestamp recording. This algorithm is designed to address these issues. Additionally, it is adaptable for media that can be viewed as a sequence of frames, such as videos.
Explanation
Fundamental Concepts
We use the built-in CPU clock which monitors the time elapsed since the music starts playing. This clock giving the current time is called
clockCurrent, hereinafter referred to asclockCR, while the clock at the moment the music starts playing is calledclockStartpoint, referred to asclockSP.clockStartpoint := clockCurrentis always assigned at the very moment the music starts or restarts playing. This is true for both initial play and mid-play resumption (breakpoint).ps-rsis an abbreviation forpause-resume. It is used to indicate the time sequence relationship between the interface signal and the media service. The explaniation of PS-RS model is provided below.
PS-RS Model
There are three variables in total:
start_time,clockCR,clockSP.start_timeis used by ffmpeg-like backends to play the audio from a specific timestamp.Sequence Diagram
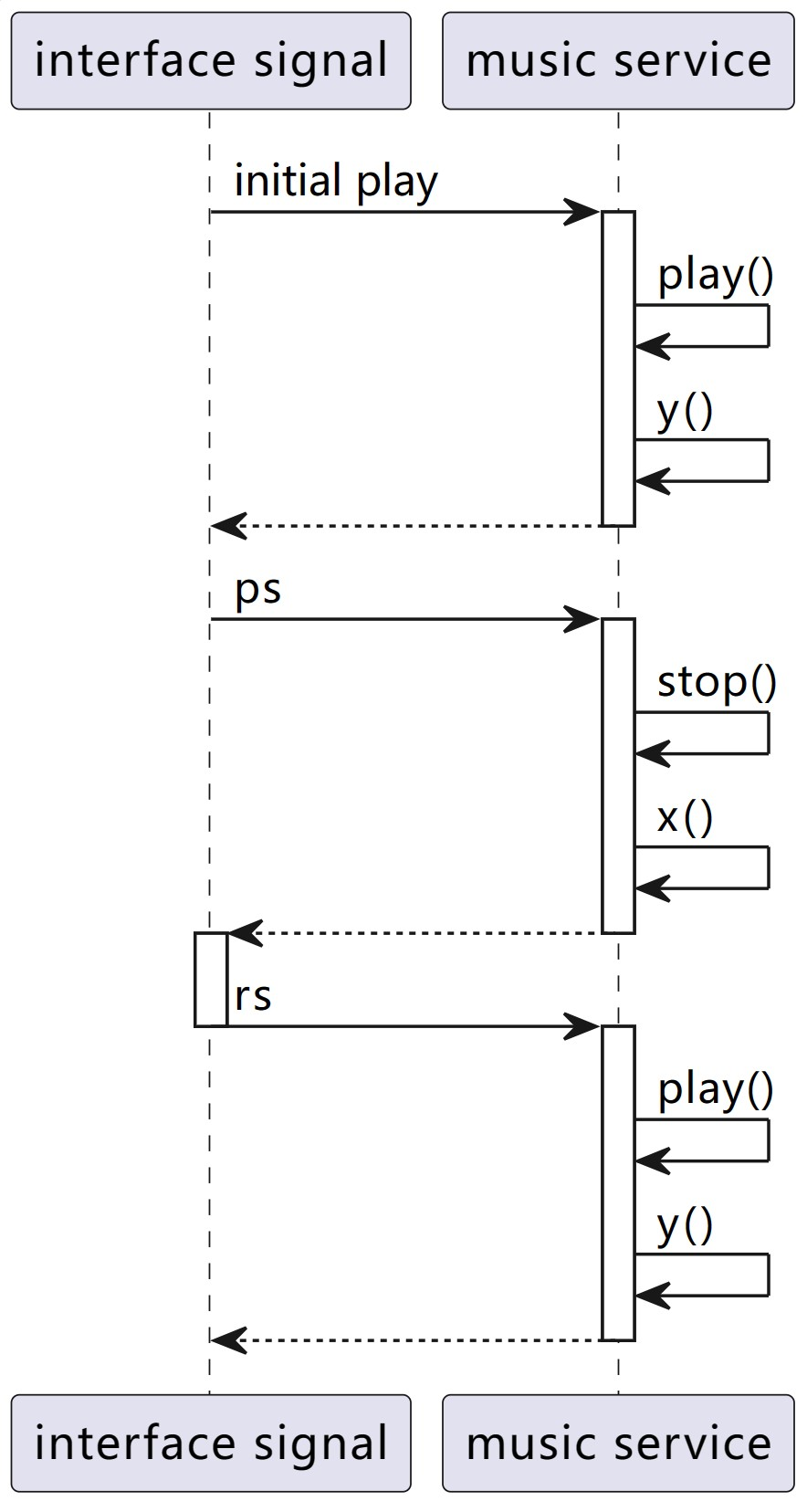
x: start_time += clockCR - clockSPy: clockSP := clockCRWe then use timer diagram for further explanation.
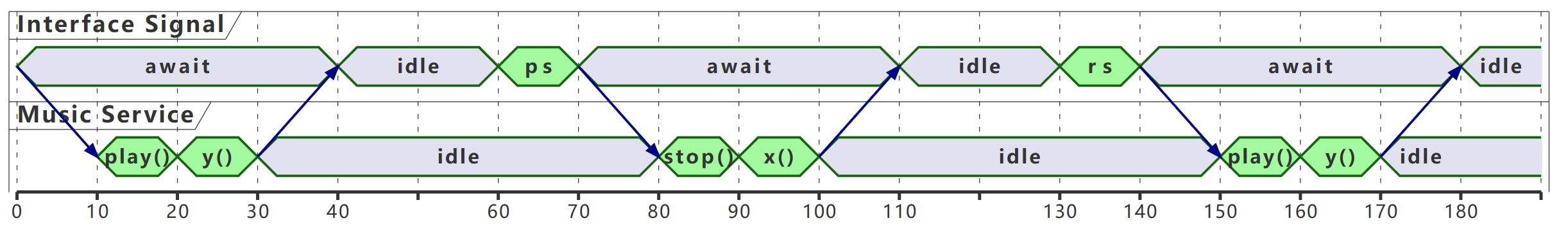
Case Check
Case 1
- pause at 5s.
- wait for 10s.
- resume, then pause again after another 5s.
- wait for 10s.
- resume.
Case 2 (Special Case)
- pause at 5s.
- resume immediately after pausing. (indicating a 0-second ps-rs interval)
- pause again after 5s.
- resume immediately after pausing again.